|
|
点击左上方蓝色“一口Linux”,选择“设为星标”
第一时间看干货文章
?【干货】嵌入式驱动工程师学习路线?【干货】Linux嵌入式知识点-思维导图-免费获取?【就业】一个可以写到简历的基于Linux物联网综合项目?【就业】找工作简历模版
2ewtzdapr5h64062959234.gif
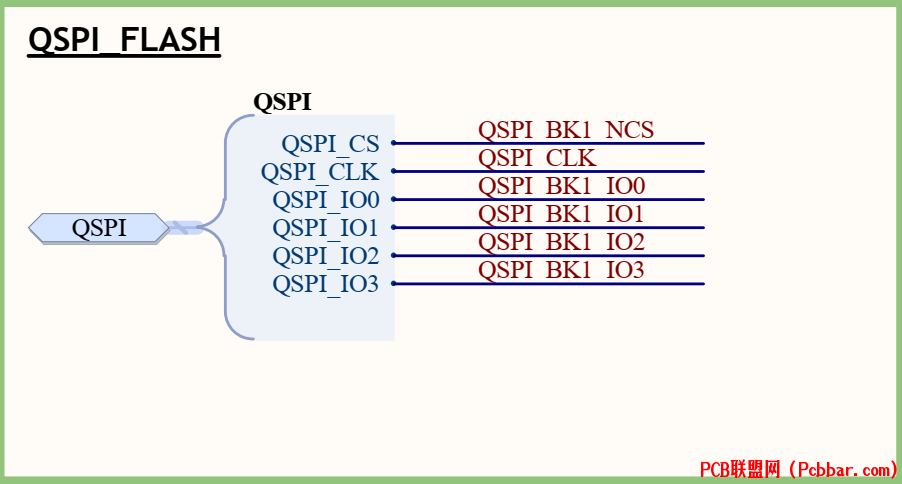
需求: 一款基于zynq架构的产品,只有qspi flash,并没有其他的存储设备,
现在的要求固化某个应用程序app,设置开机启动.
0ry13gd1uox64062959334.png
但是根据厂家提供的sdk,编译出的镜像重启后,文件系统的内容都会还原,
之前的方案是每次都要把程序放到buildroot下,
然后重新编译,将rootfs、内核镜像、设备树打包到image.ub.bin中,
然后用jtag重新烧录到flash中。
这很不合理,所以要我们需要对flash进行分区,
然后将需要固化的程序通过flashcp烧写到flash中,然后在用dd命令导出该文件。
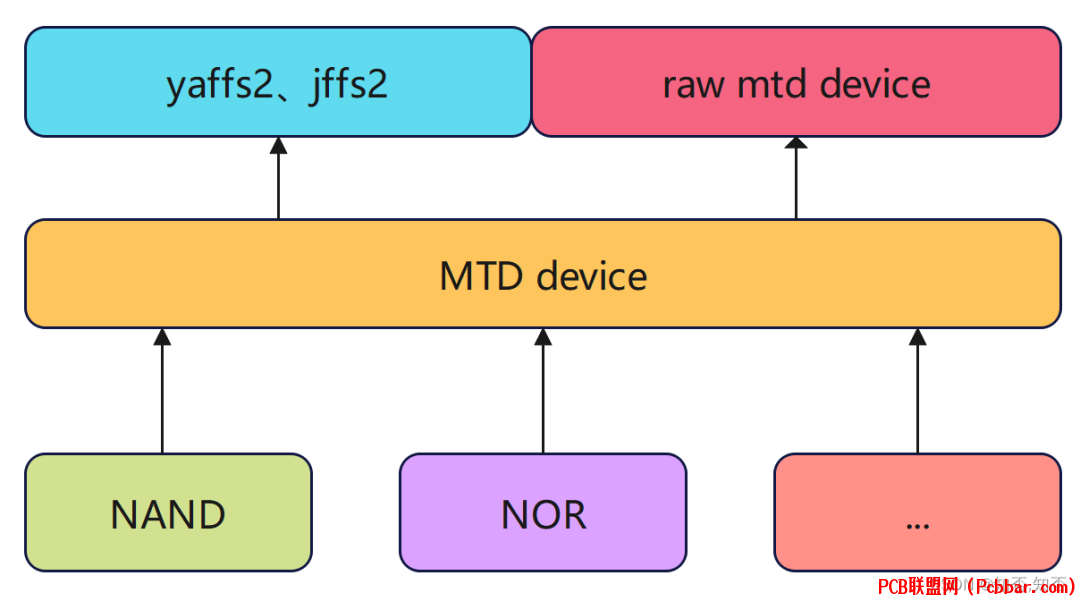
0. MTD基础 该操作依赖linux的MTD子系统。
MTD(Memory Technology Device)是内存技术设备,它为原始闪存设备(例如NAND,OneNAND,NOR 等)提供了一个抽象层。
这些不同类型的Flash都可以使用相同的API。
通常内核都默认支持MTD驱动。
hgkjalyivlp64062959434.png
MTD字符设备-通常称为**/dev/mtd0,/dev/mtd1**等。
这些字符设备提供对原始闪存的I/O访问。
它们支持许多ioctl调用,用于擦除擦除块,将其标记为不良或检查擦除块是否不良,获取有关MTD设备的信息等。
sysfs接口,它提供有关系统中每个MTD设备的完整信息。 此接口易于扩展,并且鼓励开发人员尽可能使用sysfs接口,而不是较旧的ioctl或/proc/mtd接口。
mtd子系统的sysfs接口已在内核中进行了说明,当前可在Documentation/ABI/ testing/sysfs-class-mtd中找到。
/proc/mtd proc文件系统文件提供常规的MTD信息。 这是旧版界面,而sysfs界面提供了更多信息。
MTD子系统支持带有软件和硬件ECC的 raw NAND闪存,OneNAND闪存,CFI(通用闪存接口)NOR闪存以及其他类型的闪存。
1. 查看qspi flash大小 进入uboot
fmsh> sf probe 0
SF: Detected n25q256 with page size 256 Bytes, erase size 4 KiB, total 32 MiB
该命令式查看设备信息。
可以看到qspi flash容量为32MB,即0x1E84800
2. 需要固化镜像分区地址设置 一口君使用的平台需要固化2个文件:cfg(存储配置信息)、app(可执行程序)
加上必须烧录的boot.bin、image.ub.bin,一共有4个文件,
所以我们需要配置4个分区。
1) boot.bin、image.ub.bin地址其中boot.bin包含了fpga的ip核和启动必要的文件信息,地址固定为0
image.ub.bin的地址通常厂家也会给出默认地址,
进入uboot打印环境信息:
fmsh> printenv
fit_size=0x153f000
flash_off=0x500000
load_addr=0x2000000
qspiboot=echo Copying FIT from SPI flash to RAM...
&& sf probe && sf read ${load_addr} ${flash_off} ${fit_size} && bootm ${load_addr}
echo Copying FIT from SPI flash to RAM... :
打印提示信息
sf probe:
查看设备硬件信息
sf read ${load_addr} ${flash_off} ${fit_size},
从flash地址flash_off开始读取fit_size个字节到ram地址load_addr
bootm ${load_addr}:
启动内核
可以看到flash地址是flash_off:0x500000
2) 分区划分那现在我们就可以给这4个文件设置分区信息了
镜像文件实际大小(hex)起始地址offset块数boot.bin3D09000x000000x50000061-80image.ub.binD59F800x5000000x1100000214-272cfg.bin2000x16000000x100001app.bin78000x16100000x300003注意:
offset大小必须是 0x10000整数倍,这个是擦除的最小单位-块。
每个分区大小结合要固化的程序,合理分配,既要考虑后面程序升级需要预留足够空间,也不要太大,造成浪费
分区划分不能超过flash最大值32M
3. 设备树 flash分区设备树说明如下:
Documentation\devicetree\bindings\mtd\partition.txt
Fixed Partitions
================
Partitions can be represented by sub-nodes of a flash device. This can be used
on platforms which have strong conventions about which portions of a flash are
used for what purposes, but which don't use an on-flash partition table such
as RedBoot.
The partition table should be a subnode of the flash node and should be named
'partitions'. This node should have the following property:
- compatible : (required) must be "fixed-partitions"
Partitions are then defined in subnodes of the partitions node.
For backwards compatibility partitions as direct subnodes of the flash device are
supported. This use is discouraged.
NOTE: also for backwards compatibility, direct subnodes that have a compatible
string are not considered partitions, as they may be used for other bindings.
#address-cells & #size-cells must both be present in the partitions subnode of the
flash device. There are two valid values for both:
: for partitions that require a single 32-bit cell to represent their
size/address (aka the value is below 4 GiB)
: for partitions that require two 32-bit cells to represent their
size/address (aka the value is 4 GiB or greater).
Required properties:
- reg : The partition's offset and size within the flash
Optional properties:
- label : The label / name for this partition. If omitted, the label is taken
from the node name (excluding the unit address).
- read-only : This parameter, if present, is a hint to Linux that this
partition should only be mounted read-only. This is usually used for flash
partitions containing early-boot firmware images or data which should not be
clobbered.
- lock : Do not unlock the partition at initialization time (not supported on
all devices)
我们只需要关注分区的子节点说明即可:reg
描述某个flash分区的offset和sizelabel(可选)
分区名字read-only(可选)
该分区只读
[/ol]根据前面所有分析内容,最终我们修改设备信息如下:
&qspi0 {
status = "okay";
flash0: s25fl256s@0 {
compatible = "spi-flash","spansion,s25fl256s1", "jedec,spi-nor";
reg = ; /* chip select */
spi-max-frequency = ;
m25p,fast-read;
page-size = ;
block-size = ; /* 2^16, 64KB */
cdns,read-delay = ;
cdns,tshsl-ns = ;
cdns,tsd2d-ns = ;
cdns,tchsh-ns = ;
cdns,tslch-ns = ;
#address-cells = ;
#size-cells = ;
partition@BOOT {
label = "boot";
reg = ;
};
partition@uimage.ub {
label = "uimage.ub";
reg = ;
};
partition@prm {
label = "cfg";
reg = ;
};
partition@kk_ap {
label = "app";
reg = ;
};
};
};
重新编译rootfs打包后重新启动即可。
4. 查看分区信息 # cat /proc/mtd
dev: size erasesize name
mtd0: 00500000 00010000 "boot"
mtd1: 01100000 00010000 "uimage.ub"
mtd2: 00010000 00010000 "cfg"
mtd3: 00030000 00010000 "app"
# ls /dev/mtd* -l
crw------- 1 root root 90, 0 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd0
crw------- 1 root root 90, 1 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd0ro
crw------- 1 root root 90, 2 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd1
crw------- 1 root root 90, 3 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd1ro
crw------- 1 root root 90, 4 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd2
crw------- 1 root root 90, 5 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd2ro
crw------- 1 root root 90, 6 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd3
crw------- 1 root root 90, 7 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtd3ro
brw------- 1 root root 31, 0 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock0
brw------- 1 root root 31, 1 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock1
brw------- 1 root root 31, 2 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock2
brw------- 1 root root 31, 3 Jan 1 00:00 /dev/mtdblock3
/dev/mtd0,/dev/mtd0ro,/dev/mtdblock0代表的是同一个MTD分区,但是**/dev/mtd0,/dev/mtd0ro都是字符设备,其中/dev/mtd0ro是只读字符设备,/dev/mtdblock0是块设备。
常见的mtd-utils,nand_write等工具只能操作/dev/mtdX**字符设备,因为只有字符设备才支持ioctl操作。
5. 拷贝读取 MTD 分区 查看 MTD 分区
cat /proc/mtd擦除 MTD 分区
flash_eraseall /dev/mtdX
擦除/dev/mtd0分区的第1块数据。
flash_erase /dev/mtd0 0x0 1
写 MTD 分区 NOR Flash
flashcp /tmp/mtd.bin /dev/mtdX写 MTD 分区 NAND Flash
nandwrite /tmp/image.bin /dev/mtdX读 MTD 分区
dd if=/dev/mtdX of=/tmp/mtd.bin
a) 烧写cfg.bin文件到mtd2首先需要下载文件导开发板,可以用sd卡、网口(tftp)、串口(rz命令),根据自己的开发板资源。
执行下面命令烧录:
flash_erase /dev/mtd2 0x0 1
flashcp cfg.bin /dev/mtd2
导出分区文件
dd if=/dev/mtd2 of=/mnt/cfg.bin
b) 烧写app.bin到mtd3flash_erase /dev/mtd3 0x0 3
flashcp app /dev/mtd3
导出分区文件
dd if=/dev/mtd3 of=/mnt/app.bin
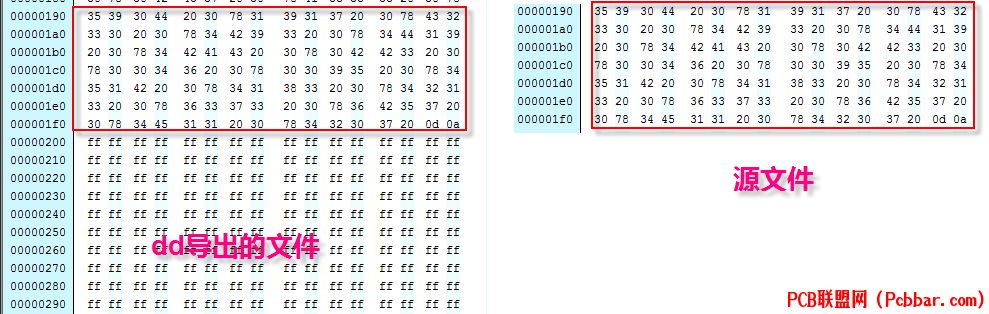
6. 还原文件 注意导出的文件除了我们烧录的文件之外,
尾部还有多余FF,所以还需要去掉这些多余的部分,
所以我们必须要还原文件。
如下图所示:
uznlgrbhsff64062959534.png
【文件必须以二进制形式打开才能看到,彭老师用的Hex Editor Neo】
p31e0hh2xyd64062959634.png

下载地址:
https://hhdsoftware.com/free-hex-editor
还原文件有很多方法,一口君自己写了个小程序,
原理:
逐字节读取文件,然后判断是否是0xFF,连续读取到16个0xff(防止文件中也由多个0XFF出现),
则认为读到了有效文件尾部,记录有效文件长度,然后根据该长度,复制成最终文件,该文件就是我们所需要的最终文件。
源码:#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int fd_p;
int fdw_p;
unsigned char c;
int count = 0;
int pos = 0;
int i;
if(argc != 3)
{
printf("argument error
");
for(int i = 0; i printf("argv[%d] = %s
", i, argv);
}
}
fd_p = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if(fd_p 0){
printf("open file %s failed
", argv[1]);
return -1;
}
fdw_p = open(argv[2], O_RDWR | O_CREAT);
if(fdw_p 0){
printf("open file %s failed
", argv[2]);
return -1;
}
while(1){
read(fd_p, &c, 1);
if(c == 0xff){
count++;
if(count >= 16){
break;
}
}
else{
count = 0;
}
pos++;
}
lseek(fd_p, SEEK_SET, 0);
for(i=0; i-15; i++){
read(fd_p, &c, 1);
write(fdw_p, &c, 1);
}
return 0;
}
测试: |
|
 /1
/1